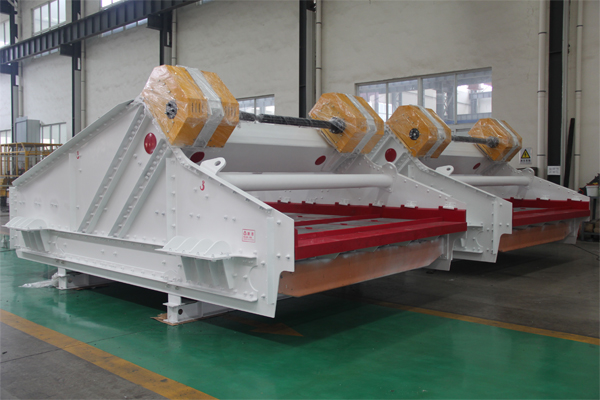
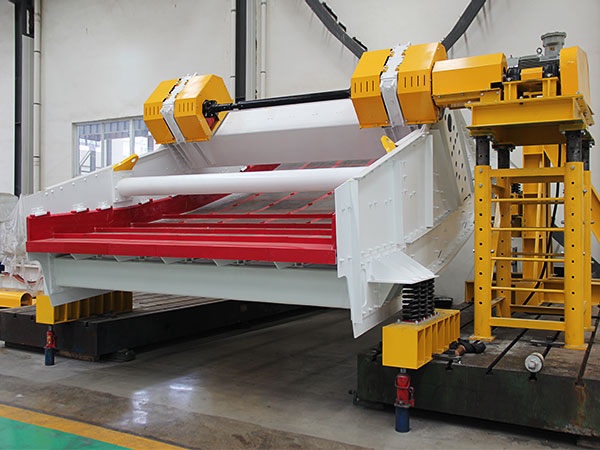
How to install the screen of linear vibrating screen
The installation of the screen on a linear vibrating screen is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in material separation. A well-installed screen minimizes issues like material clogging, screen tearing, or improper material classification.
How to install the screen of linear vibrating screen

1. Preparation
Safety Precautions: Before starting, ensure the power to the vibrating screen is disconnected, and all safety procedures are followed to prevent accidents.
Check the Screen Deck: Inspect the screen deck for any wear, damage, or debris. Clean it thoroughly to ensure a smooth installation.
Check the Screen Size: Ensure the screen mesh size and dimensions are appropriate for the machine and the material to be processed.
2. Screen Frame Assembly
Remove the Old Screen (if replacing): If you are replacing an old screen, carefully remove it by loosening any clamps, bolts, or fasteners securing it to the frame.
Screen Frame Condition: Inspect the screen frame for any wear or damage. Repair or replace damaged parts if necessary to ensure the screen is mounted securely.
3. Position the Screen
Correct Alignment: Place the new screen mesh over the screen frame or screen deck, making sure it is aligned properly. The screen must cover the entire frame evenly without stretching or overlapping.
Ensure Tension: The screen should have uniform tension across its surface to prevent sagging or loose areas, which can affect material flow and separation efficiency.
For tensioned screens, pull the screen tightly in both directions to ensure it’s uniformly taut.

4. Secure the Screen
Clamping Bars or Fasteners: Use clamping bars, bolts, or other fastening mechanisms to secure the screen to the vibrating screen’s frame. Ensure that the screen is tightly secured to prevent it from loosening during operation.
Clamping Sequence: When tightening the clamps or fasteners, start from one side and move gradually to the other, alternating sides to apply even tension across the entire screen.
Avoid over-tightening the fasteners, as this can damage the screen or cause uneven tension.
5. Check Tensioning and Alignment
Test the Tension: Once secured, check the screen tension by pressing lightly on different sections of the screen. It should feel equally taut throughout without any slack.
Re-adjust if Necessary: If there are any areas with slack or improper tension, loosen the clamps slightly, adjust the screen, and then re-tighten until the tension is even.
Check Alignment: Ensure the screen is perfectly aligned with the screen frame, with no overhanging or misaligned edges.
6. Inspection of Side Seals and Gaskets
Side Seals: Verify that the side seals are intact and in the correct position to prevent leakage of material outside the screen.
Gaskets: Ensure that any gaskets between the screen and the frame are properly fitted and undamaged, as this will prevent vibration-related wear and material leakage.
7. Pre-Operation Check
Visual Inspection: After securing the screen, visually inspect the entire screen deck to ensure there are no visible gaps, wrinkles, or improper installations.
Manual Testing: Rotate the machine manually (if possible) or simulate the screen motion without loading material to ensure the screen remains firmly in place and operates smoothly without any unusual noises or movements.

8. Run the Machine
Test with Material: Start the machine and introduce a small amount of material to check the screen’s performance. Monitor for any irregularities like improper material flow, vibrations, or noise, which may indicate improper screen installation.
Vibration Check: Ensure the machine vibrates uniformly and the screen is not shaking excessively, as this could indicate poor tension or installation errors.
9. Regular Inspection and Maintenance
Monitor Screen Condition: Regularly inspect the screen for wear and tear, material buildup, or clogging. Screens should be cleaned or replaced as necessary to maintain efficiency.
Check Fasteners: Periodically check the clamping mechanisms to ensure they remain tight during operation.
By following these steps, you can ensure that the screen on a linear vibrating screen is installed correctly, which will improve screening efficiency, prolong the lifespan of the screen, and prevent operational issues.