Why does the material on the linear vibrating screen deviate?
The deviation of material on a linear vibrating screen can occur for several reasons, affecting the efficiency of the screening process. When the material does not flow uniformly across the screen, it can lead to improper screening, clogging, and reduced performance.
Linear vibrating screen material deviation
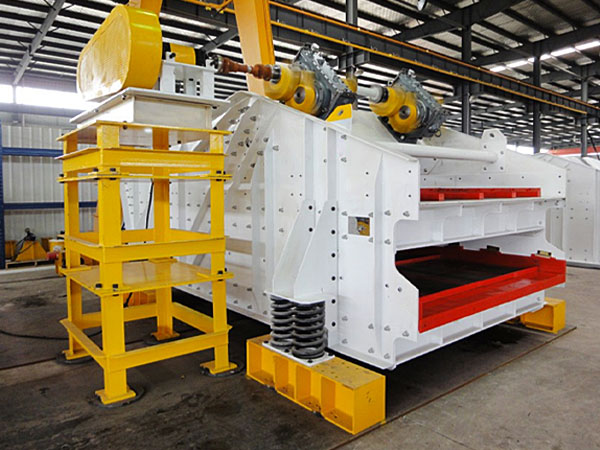

1. Uneven Loading of Material
Cause: If the material is not fed uniformly across the width of the screen, one side may have more material than the other, leading to uneven distribution.
Solution: Ensure the material is fed evenly across the entire width of the vibrating screen. This can be achieved by adjusting the feeding mechanism, such as using a properly sized feeder or installing a distributor.
2. Imbalance of the Vibrating Motors
Cause: Linear vibrating screens typically use dual motors that must operate in sync. If one motor is running at a different speed, amplitude, or direction than the other, it can create an imbalance in vibration, causing material to shift to one side.
Solution: Check the alignment, speed, and angle of both motors to ensure they are synchronized and generating equal force. Correcting the imbalance will restore uniform material flow.
3. Incorrect Motor Position or Angle
Cause: The installation angle of the vibrating motors can influence the direction of material flow. If the angles of the motors are incorrect or inconsistent, the material may move in an undesired direction, causing deviation.
Solution: Adjust the angle of the motors according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Most linear screens are designed to work with a specific motor angle to achieve optimal material flow.
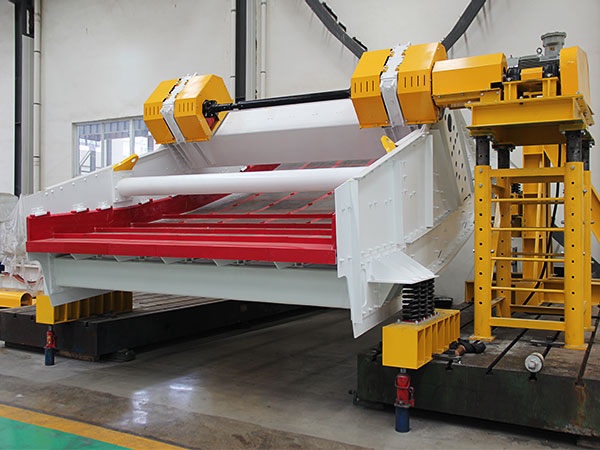

4. Uneven Tension of the Screen Mesh
Cause: If the screen mesh is not tensioned evenly across the frame, it can cause parts of the screen to vibrate more or less than others. This can lead to uneven material distribution, with some areas allowing more material to pass through and others pushing it to the sides.
Solution: Check the tension of the screen mesh and adjust it evenly across the entire screen surface. Regular maintenance to keep the mesh properly tensioned can prevent this issue.
5. Damage or Wear to Screen Deck
Cause: If the screen deck has become damaged or worn out, it may not provide a consistent surface for the material to move across, leading to deviation or material accumulation on one side.
Solution: Inspect the screen deck for signs of wear, tears, or other damage. Replace or repair the screen deck as necessary to restore a smooth, uniform surface.
6. Inconsistent Vibrating Force
Cause: Vibrating force needs to be consistent across the entire screen. If there are inconsistencies due to motor misalignment, improper installation, or mechanical defects, the material may not flow uniformly, leading to deviation.
Solution: Ensure that the vibration force is consistent and evenly distributed by checking the alignment, motor power, and installation of the entire system.
7. Improper Slope Angle
Cause: The inclination or slope of the vibrating screen plays a key role in material flow. If the slope is too steep or too shallow, it can cause uneven material distribution.
Solution: Adjust the inclination angle of the screen according to the material characteristics and required processing speed. A properly inclined screen helps material flow evenly across the surface.
8. Vibration Damper Issues
Cause: Damper springs or shock absorbers are responsible for balancing the screen’s vibration. If one or more dampers are worn out or misaligned, the screen may vibrate unevenly, causing material to move erratically and deviate.
Solution: Inspect and replace any worn or damaged dampers. Properly balanced dampers are essential for maintaining uniform vibration and material flow.
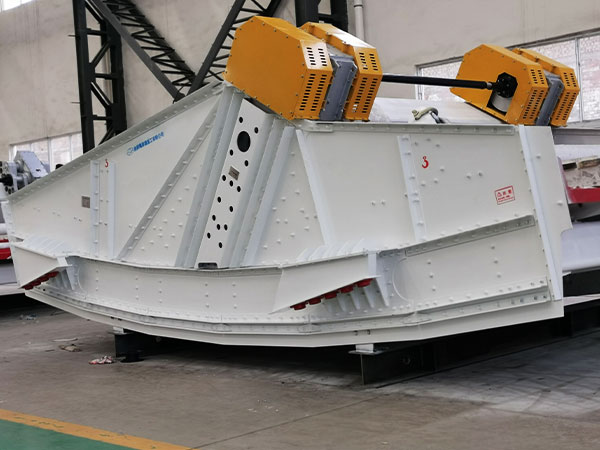

9. Material Characteristics
Cause: The physical properties of the material, such as particle size, moisture content, or stickiness, can affect how it moves across the screen. Materials that are too wet, sticky, or have varying sizes may clump together and flow unevenly.
Solution: Consider pre-treating the material (e.g., drying or de-lumping) before feeding it onto the screen. You can also use appropriate screen mesh sizes or install a secondary screening system to handle materials with challenging characteristics.
10. External Vibrations or Environmental Factors
Cause: External vibrations from nearby equipment or structural movement can affect the operation of the vibrating screen, leading to material deviation.
Solution: Isolate the vibrating screen from external sources of vibration and ensure that the mounting structure is stable and not causing interference.
11. Frame or Structure Misalignment
Cause: If the screen’s frame or supporting structure is not properly aligned or leveled, it can lead to uneven vibration and material flow.
Solution: Check the alignment and leveling of the vibrating screen and its supporting structure. Adjust the leveling bolts or foundation to ensure the screen is properly positioned.
12. Improper or Worn Out Screen Media
Cause: The screen media (wire mesh or perforated plate) may become clogged, worn, or damaged, causing uneven material distribution.
Solution: Regularly clean and inspect the screen media. Replace worn-out or damaged media to ensure smooth material flow and proper screening performance.
Conclusion
To ensure that the material on a linear vibrating screen does not deviate, it’s crucial to maintain proper motor synchronization, uniform loading, screen tension, and correct installation angles. Regular inspections and maintenance are key to preventing material deviation and ensuring efficient screening performance.