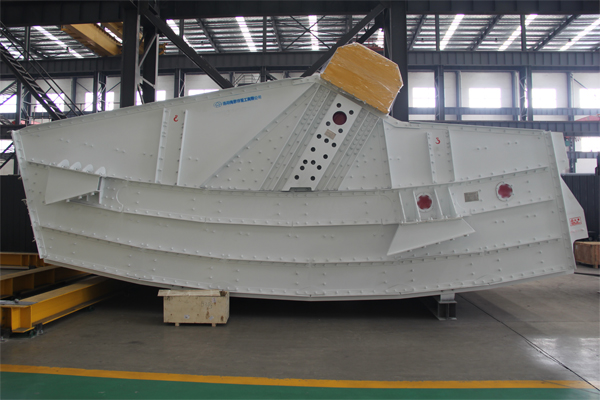
Vibrating screens are widely used in various industries for separating materials by size, but they can encounter several common faults that can impact their performance. Here are some of the most common issues and their solutions.
Common Problems and Solutions of Vibrating Screen
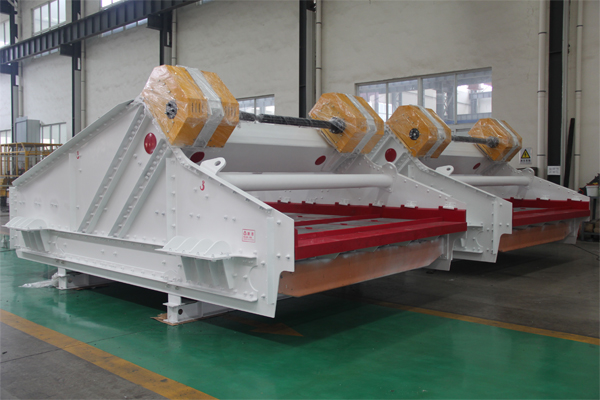

1. Excessive Vibrations
Causes:
Unbalanced Screen: Imbalance in the screen due to improper loading or wear and tear of components like the vibrating motor.
Loose Bolts or Fasteners: Over time, bolts or fasteners may loosen, causing instability.
Worn Bearings: Bearings can wear out, leading to excessive vibrations.
Solutions:
Check and Balance the Screen: Ensure that the load is evenly distributed across the screen. Regularly inspect and balance the vibrating motor.
Tighten Bolts: Inspect and tighten all bolts and fasteners regularly.
Replace Bearings: If bearings are worn, replace them promptly to avoid further damage.
2. Screen Overloading
Causes:
Excessive Feed Rate: Feeding more material than the screen can handle.
Material Buildup: Accumulation of material on the screen surface, leading to reduced screening efficiency.
Solutions:
Regulate Feed Rate: Adjust the feed rate to ensure that the screen is not overloaded.
Regular Cleaning: Regularly clean the screen surface to remove any buildup and maintain efficiency.

3. Screen Blinding
Causes:
Fine Particles: Fine materials or sticky particles can clog the screen openings, preventing proper material separation.
Moisture Content: High moisture content in the material can lead to blinding.
Solutions:
Use Anti-Blinding Devices: Install anti-blinding devices like ball trays or sliders to help clear blocked openings.
Adjust Moisture Levels: Reduce the moisture content of the feed material if possible or consider pre-drying the material.
4. Screen Frame Damage
Causes:
Overloading or Impact: Excessive load or impact from large particles can cause the screen frame to crack or bend.
Fatigue: Repeated stress over time can lead to metal fatigue and eventual failure.
Solutions:
Inspect and Repair: Regularly inspect the screen frame for signs of wear and repair or replace damaged sections as needed.
Reduce Impact: Install impact protection or reduce the size of the feed material to minimize damage.

5. Inconsistent Material Flow
Causes:
Improper Installation: Incorrect installation or leveling of the vibrating screen.
Uneven Wear: Uneven wear of screen components, such as the screen mesh or frame.
Solutions:
Check Installation: Ensure the vibrating screen is installed correctly and level.
Replace Worn Components: Regularly inspect and replace worn screen mesh or other components to maintain even material flow.
6. Reduced Screening Efficiency
Causes:
Worn or Damaged Screen Mesh: Over time, the screen mesh can wear out or tear, reducing screening efficiency.
Incorrect Vibrating Parameters: Incorrect amplitude, frequency, or angle of inclination.
Solutions:
Replace Screen Mesh: Regularly inspect and replace the screen mesh if it is worn or damaged.
Adjust Vibrating Parameters: Fine-tune the vibrating parameters to optimize screening efficiency. Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for proper settings.

7. Noise Issues
Causes:
Loose Components: Loose bolts, screen mesh, or other components can cause excessive noise.
Worn Parts: Worn bearings or other components can lead to noisy operation.
Solutions:
Tighten and Secure Components: Regularly inspect and tighten any loose parts.
Replace Worn Parts: Replace any worn bearings or other components to reduce noise levels.
8. Motor or Drive Problems
Causes:
Overheating: The motor may overheat due to overloading or lack of proper ventilation.
Electrical Issues: Wiring problems or issues with the control panel.
Solutions:
Ensure Proper Ventilation: Make sure the motor is adequately ventilated to prevent overheating.
Inspect Electrical Systems: Regularly check the wiring and control systems for any faults and repair as necessary.
Regular Maintenance Tips
Routine Inspections: Regularly inspect all components of the vibrating screen, including the screen mesh, frame, bearings, and motor.
Lubrication: Ensure that all moving parts, especially bearings, are adequately lubricated according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Alignment Checks: Periodically check the alignment of the motor and screen frame to ensure they are properly synchronized.
By addressing these common faults promptly and performing regular maintenance, the efficiency and longevity of vibrating screens can be significantly improved.